Circadian rhythm, also known as the sleep-wake cycle, is an internal monitoring clock that runs continuously to maintain the balance between the states of alertness and sleepiness.
Simply, it regulates the sleep pattern of an individual. The circadian rhythm is not only a characteristic feature of human beings, but it is also found in animals. The study of circadian rhythm, called chronobiology, is an important area of interest as it provides deep insights into the importance of sleep and its impact on an individual.
How Does Circadian Rhythm Work?
The maintenance of the circadian rhythm is a function of the suprachiasmatic nucleus, which is located in the hypothalamus of the brain. It receives the light signals from the retina of the eyes and then modulates this information to various parts of the brain.
One of the areas of the brain is the pineal gland, which upon receiving stimulus from the suprachiasmatic nucleus, releases melatonin.
Melatonin is the hormone responsible for initiating sleep.
The signals perceived and sent by the suprachiasmatic nucleus vary throughout the day. Usually, the circadian rhythm coincides with the sun’s cycle. During the daytime, when the light is there, inhibitory signals are sent to the pineal gland causing it to stop the release of melatonin, while during the night, in the absence of light, the excitatory signals cause the pineal gland to release melatonin.
However, it is important to note that the circadian rhythm of an individual varies with time and their sleeping and awakening routine. for this reason, it is advised to avoid screen use before bedtime, as it interferes with melatonin secretion, ultimately disturbing the sleep.
What Happens When One’s Routine is Not Aligned with the Circadian Rhythm?
As mentioned earlier, the circadian rhythm of every individual is different from the other, and is largely based on their routine. The frequent changing of routine, particularly in those having night shifts two or more days apart or alternative working hours, results in the chronic disturbance of the circadian rhythm.
The body is unable to adapt to a specific routine, the lifestyle and the circadian rhythm become misaligned, which eventually leads to chronic sleep disturbances. This causes serious negative effects on health, disturbing immune, reproductive, endocrine, gastrointestinal, and cardiovascular systems.
Now, even if a person tries to get a full night’s sleep, it will result in a poor distribution of sleep stages, as the sleep period is suboptimal for that individual’s chronotype. It can be understood by an example, that often after sleeping for long hours, one may feel tired and drowsy. This is because their sleep hours do not match with their circadian rhythm.
Relationship Between Sleep and Stress
Upon exposure to stress, the body produces a hormone called the ‘cortisol stress hormone’, which prepares it for a fight and flight response. The exact mechanism by which stress affects circadian rhythm is not well-understood, but it has been proved that stress hormone does alter the biological clock.
The complex relationship between stress and sleep is such a way that both adversely affect each other. Not having adequate sleep increases the stress level of the body, while, the stress itself is a cause of insomnia and disturbed sleep.
Hazards of not getting enough sleep
Lack of sleep has severe health consequences. It increases the risk of endocrine, cardiovascular and psychological illnesses. The overall short-term effects are:
- Negative mood
- Low energy
- Difficulty concentrating
- Inability to perform well
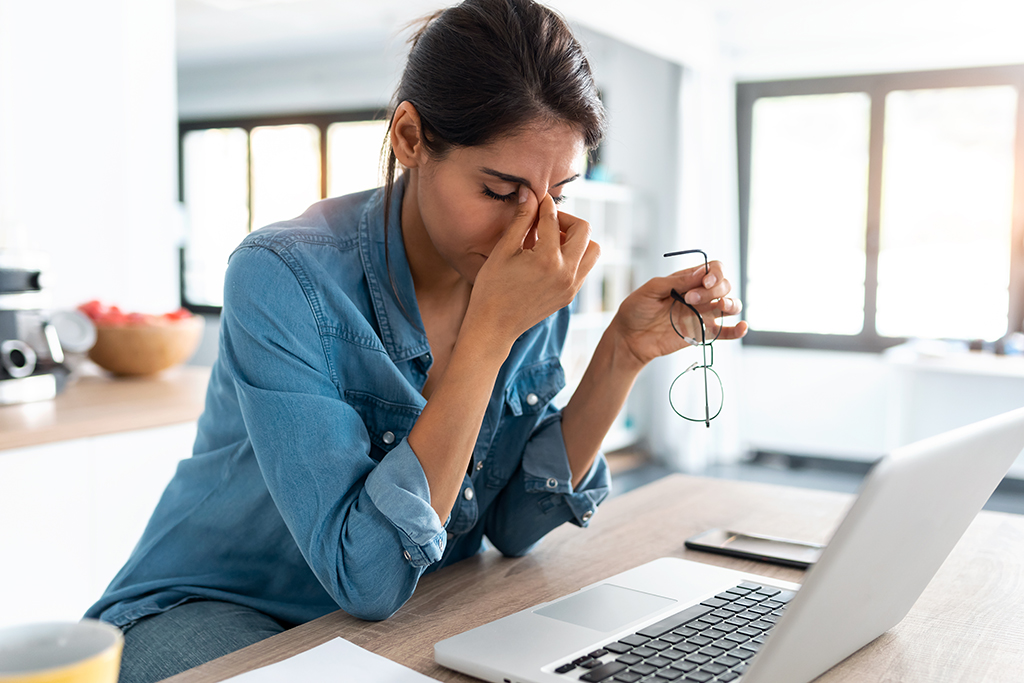

The long-term adverse effects of not getting enough sleep have a variable clinical presentation. Sleep is essential for the brain to work properly. During sleep, the brain prepares the body for the next day routine, resynchronizes its connections, removes toxins, and improves its neuronal circuits.
Lack of sleep disturbs healthy brain functioning. Adequate sleep is also required for enhancing memory, learning new skills, problem-solving, decision making, and paying attention. Sleep deficiency negatively impacts all these. In the worst-case scenario; it may lead to depression and suicidal ideation.
In children, enough sleep is needed for adequate growth. During sleep, the body releases a hormone called the growth hormone. It is required for proportional growth of muscles, bones, and other tissues of the body in children. It also has some metabolic role. Sleep deficiency in children thus results in stunted and retarded growth.
Sleep also affects the endocrine functioning of the body. It maintains the balance between ghrelin and leptin, the two hormones that produce the feeling of being hungry and full, respectively. The disturbance of this healthy relationship results in the development of eating disorders.
Furthermore, it alters the interaction between the body and the insulin hormone. Sleep deficiency results in increased levels of blood glucose, and chronic cases may lead to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
In addition, sleep deficiency is directly related to the risk of development of heart disease, kidney disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, and stroke. The immune system may also be affected because of chronic sleep deprivation.
The Importance of Getting Adequate Sleep:
The importance of getting adequate and routinely sleep can be emphasized by the following factors:
- Enough sleep is important for better concentration, cognition, and productivity.
- Sleep helps in the consumption of fewer calories intake, as it affects the pattern of appetite producing hormones. Getting adequate sleep improves the body’s ability to properly regulate food intake.
- Sufficient sleep helps boost athletic performance. A sleep of 7-9 hours is highly beneficial for adults and is as important as the consumption of calories and nutrients. It energizes the person, improves coordination, fastens the speed, and enhances mental functioning.
- Sleep quality and quantity affect heart physiology. Getting proper sleep reduces the risk of heart diseases. It also helps in lowering blood pressure.
- Sleep is important for emotional and social intelligence. The emotional empathy of an individual decreases with the declining quality and quantity of sleep.
- Adequate sleep reduces the risk of depression.
- Getting enough sleep also helps in reducing inflammation in the body, and may help in alleviating symptoms of auto-inflammatory diseases. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to the foreign particles that invade it. Sometimes, the body mistakenly recognizes its own components as a foreign body which may trigger an unnecessary inflammatory response, resulting in widespread destruction. These conditions are termed as auto-inflammatory disorders. getting proper sleep can help improve these conditions.